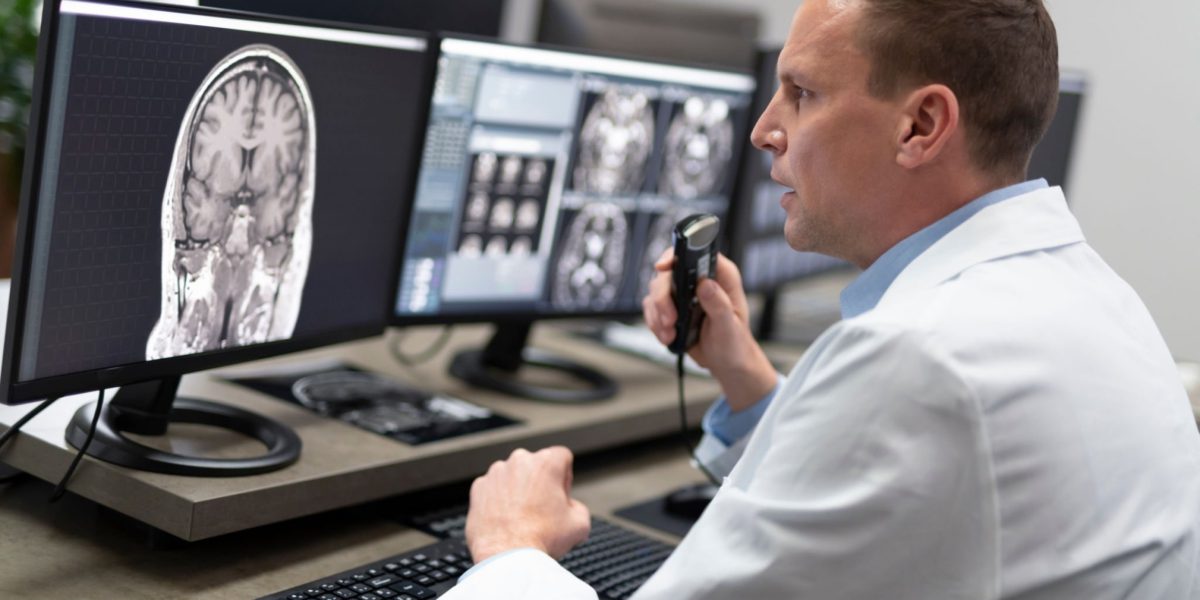
Introduction
Radiology is a specialized field of medicine that focuses on the use of medical imaging techniques to diagnose and treat various diseases and conditions. It plays a crucial role in modern healthcare by providing detailed visual information about the internal structures of the human body, aiding in accurate diagnoses and treatment planning.
Medical imaging techniques used in radiology include:
X-ray: X-rays are the oldest and most commonly used form of medical imaging. They use low levels of radiation to create images of bones, lungs, and other dense structures in the body. X-rays are particularly useful for diagnosing fractures, lung infections, and some forms of cancer.
Computed Tomography (CT): CT scans involve taking a series of X-ray images from different angles around the body. A computer then processes these images to create cross-sectional pictures, allowing for detailed examination of organs, blood vessels, and tissues. CT scans are used to diagnose conditions such as tumors, vascular diseases, and internal injuries.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI uses a powerful magnetic field and radio waves to generate detailed images of organs and tissues. It is particularly useful for evaluating soft tissues, such as the brain, spinal cord, joints, and muscles. MRI is commonly employed to diagnose neurological disorders, musculoskeletal injuries, and abnormalities in organs like the liver and kidneys.
Ultrasound: Ultrasound imaging uses high-frequency sound waves to produce real-time images of internal organs and tissues. It is commonly used during pregnancy to monitor fetal development. Additionally, ultrasound is valuable for assessing the heart, blood vessels, and abdominal organs, and guiding minimally invasive procedures.
Nuclear Medicine: Nuclear medicine involves administering small amounts of radioactive material into the body, which is then detected by specialized cameras to create images of organs and their functioning. Techniques such as Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) and Positron Emission Tomography (PET) are commonly used to diagnose and track conditions like cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders.
Radiologists are medical doctors who specialize in interpreting these medical images and providing diagnostic reports to aid in patient care. They work closely with other healthcare professionals to determine the most appropriate imaging modality, interpret images accurately, and provide guidance for further treatment or intervention.
In recent years, there have been significant advancements in radiology, driven by technological innovations such as digital imaging, 3D reconstruction, and artificial intelligence (AI). These developments have improved image quality, reduced radiation exposure, enhanced diagnostic accuracy, and facilitated the integration of radiology with other medical specialties.
Overall, radiology plays a pivotal role in modern medicine by providing critical insights into the intricacies of the human body and enabling healthcare professionals to make informed decisions for patient care.
Radiology has evolved into a multidisciplinary field, collaborating with various medical specialties to provide comprehensive patient care. Radiologists work closely with referring physicians, surgeons, oncologists, and other specialists to understand the clinical context and tailor imaging protocols accordingly. Their expertise in interpreting medical images is vital for accurate diagnosis, treatment planning, and monitoring of patient progress.
Advancements in radiology have led to significant improvements in image quality and diagnostic capabilities. Digital imaging has replaced traditional film-based techniques, allowing for faster image acquisition, storage, and transmission. This transition has also facilitated the integration of radiology into electronic health record systems, enhancing communication and collaboration among healthcare providers.
Another exciting development in radiology is the utilization of artificial intelligence (AI) algorithms to assist in image interpretation. AI algorithms can analyze large datasets, detect patterns, and assist radiologists in identifying abnormalities. This technology has the potential to improve diagnostic accuracy, increase efficiency, and reduce the burden of repetitive tasks, allowing radiologists to focus more on complex cases and patient interaction.
Furthermore, radiology has expanded beyond traditional anatomical imaging to functional and molecular imaging techniques. Functional imaging methods, such as functional MRI (fMRI) and diffusion tensor imaging (DTI), provide insights into brain activity and connectivity. Molecular imaging techniques, like PET-CT and SPECT, allow visualization of cellular and molecular processes, aiding in the diagnosis and treatment of various diseases.
Interventional radiology is another important subspecialty within radiology. It involves using image-guided techniques to perform minimally invasive procedures, such as angioplasty, embolization, and tumor ablation. These procedures offer patients a less invasive alternative to traditional surgery, with shorter recovery times and fewer complications.
Radiology also plays a significant role in population health initiatives and public health research. By analyzing large-scale imaging data, radiologists can identify patterns and trends, contributing to the understanding of disease prevalence, risk factors, and treatment outcomes. This information can help shape healthcare policies, optimize resource allocation, and improve patient outcomes on a broader scale.
In conclusion, radiology is a dynamic and rapidly advancing field that continues to push the boundaries of medical imaging. Through its diverse imaging modalities, collaboration with other medical disciplines, and integration of cutting-edge technologies, radiology provides invaluable information that supports accurate diagnoses, precise treatment planning, and improved patient outcomes.
Common FAQs
What is the role of a radiologist?
A radiologist is a medical doctor who specializes in interpreting medical images to diagnose diseases and conditions. They work closely with other healthcare professionals to provide accurate and timely diagnoses, guide treatment decisions, and monitor patient progress.
How long does it take to become a radiologist?
Becoming a radiologist typically requires several years of education and training. After completing a bachelor’s degree, aspiring radiologists need to attend medical school, which usually takes four years. After medical school, they undergo a residency training program in radiology, which can range from four to six years. Additional fellowship training may also be pursued for subspecialization within radiology.
Is radiation used in all imaging procedures?
Radiation is not used in all imaging procedures. While X-rays and CT scans involve ionizing radiation, other imaging modalities like MRI and ultrasound do not use radiation. The choice of imaging technique depends on the specific clinical question, the body part being examined, and factors such as safety, availability, and image quality requirements.
Are imaging procedures safe?
Medical imaging procedures are generally safe when performed by trained professionals and when appropriate safety measures are followed. The level of risk associated with radiation-based imaging, such as X-rays and CT scans, is considered low, and the benefits usually outweigh the potential risks. However, pregnant women and young children may be more susceptible to radiation effects, and precautions are taken to minimize radiation exposure in these populations.
What should I expect during an imaging procedure?
The specific details of an imaging procedure will vary depending on the type of imaging being performed. Generally, you may be asked to change into a gown and remove any metal objects or jewelry that may interfere with the imaging. You will be positioned on a table or in a device specific to the procedure, and the technologist will guide you through the process. It’s important to remain still during the imaging to ensure clear and accurate images.
Will I receive the results immediately after the imaging procedure?
In most cases, the radiologist will not provide immediate results to the patient directly after the imaging procedure. The images need to be carefully reviewed and interpreted by the radiologist, who will then generate a detailed report. The report is typically sent to the referring physician, who will discuss the results with you during a follow-up appointment.
Can I request a copy of my imaging results?
Yes, you can usually request a copy of your imaging results. However, it is common practice for the results to be sent directly to your referring physician. You can discuss the process of obtaining a copy of your results with your healthcare provider or the radiology department where the imaging was performed.
It’s important to note that these answers are general and may vary depending on specific circumstances or healthcare practices. It is always recommended to consult with your healthcare provider or radiologist for personalized information and guidance related to your situation.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, radiology is a vital medical specialty that utilizes various imaging techniques to diagnose and treat diseases and conditions. Radiologists play a crucial role in interpreting medical images, providing accurate diagnoses, and collaborating with other healthcare professionals to guide patient care. The field of radiology continues to advance with technological innovations, such as digital imaging and artificial intelligence, improving image quality, diagnostic accuracy, and efficiency. With its diverse imaging modalities and multidisciplinary approach, radiology remains at the forefront of modern healthcare, unraveling the intricacies of the human body and contributing to improved patient outcomes.